Today, we are dealing with a lot of data from multiple sources and it is becoming complex to manage data. Different types of data, structured, unstructured, pictures, audios etc along with the creation of new sources of data with an increase in adoption of mobile devices and IOT. Data management is becoming a complex issue.
When we are dealing with so much information in so many different forms, it is impossible to think about data management in traditional ways. We have to think about data in different ways and that is where big data comes in. In this article, we will look at this evolution of data to big data and how and what evolved in terms of big data.
The Evolution
As with most of other technologies, the evolution in data management is also an incremental one based on its predecessors. When we look at data management evolution, we have to look at it with respect to advancements in software, hardware, storage, networking, and computing models such as virtualization and cloud computing. As all these technologies converge, it is transforming the way we manage and leverage data.
Stages of Data Management Evolution
Each evolution in data management is due to the fact that it needed to solve a specific business problem. The data management incremental evolution over the past 50 years resulted in where we are today: the Big Data era.
Stage 1: Manageable Data Structures
As technology entered the commercial market in the 1960s, companies started with storing all the data in flat files. They quickly realized that it is not the best way to store data as searching through those files is really hard and time-consuming. So, in 1970s first data management system arrived in order to store data in the form of specific structures, called relational data model and the relational database management system (RDBMS). Relational data model added a level of abstraction in the form of Structured Query Language (SQL) so that it is easier to query and search for data to satisfy growing business needs.
Stage 2: The ER Stage
With the advent of RDBMS, companies all over the world were storing more and more data and new use cases were emerging. But also emerging were issues like data storage was quite expensive, data processing and accessing was slow, data duplication was a huge issue etc.
This gave rise to the need to find new technologies to support and improve relational data model. Entity Relationship (ER) models were the next iteration.
ER Models added more abstraction layers to data in order to increase usability. In ER model, each entity was defined independently of its use. So that relationship between these entities can be created as per the need. ER model made its way to programming languages and developers were able to create more complex techniques for joining entities together.
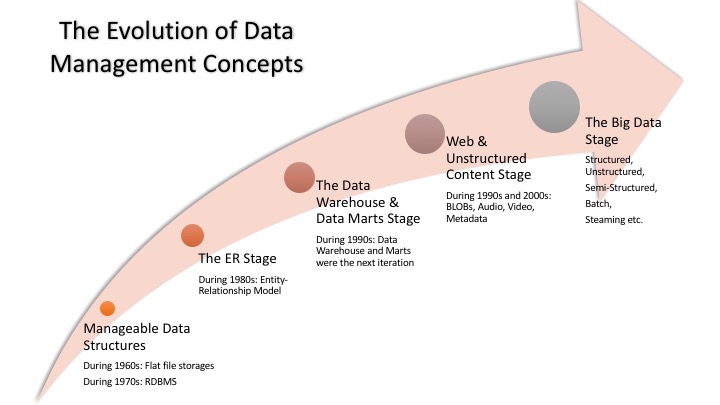
Stage 3: The Data Warehouse and Data Marts Stage
Organizations kept on adding more and more data and next problem was that organizations needed to manage the large volume of data which was growing out of control. The solution came with the next iteration in data management in the form of Data Warehouse.
Data Warehouses were commercialized in the 1990s. They enable the IT organizations to store all the data irrespective of the volume and then select the subset of the data much smaller and more focused on a particular area of the business. Even when the volume of data is too large and start impacting the speed and agility required by the business. Further refinements are then needed and these are called data marts. These data marts were focused on specific business issues and were much more streamlined and supported the business need for speedy queries than the more massive data warehouses. Since then data warehouses have evolved with emerging technologies and are taking advantages of improvements in scalability of hardware, virtualization technologies and the ability to create integrated hardware and software systems.
Stage 4: Web and Unstructured Content
With the rise in popularity of web and internet, more and more unstructured data was being created in the form of web content, images, audio, and video.
The very first solution implemented by vendors was BLOBs (Binary Large Objects). BLOB was a type where an unstructured data element would be stored in a relational database as one continuous chunk of data. This object can be labeled but we couldn’t see what was inside the object. Organizations were storing documents in BLOBs but they soon realized that is not enough, and they will need to store other content like audio, video, images more effectively.
Different solutions existed to different use cases but market evolved from these set of disconnected solutions to a more unified model that brought together these elements into a single platform that incorporated business process management, information recognition, version control, text management along with metadata. These systems solved the major problem but gave rise to new use cases and requirements. Organizations begin to understand that they need to manage a new generation of data sources with huge amount and variety of data that will need to be processed with great speed. This gave rise to next increment on data management called the era of Big Data.
Stage 5: Big Data
Big Data is an increment in data management journey in a way that it is built on top of the evolution of data management practices from the last 5 decades. But it is also a new system in a way that for the first time the cost of computing cycles and storage has reached a tipping point and with big data, it is possible to virtualize data so that it can be stored to efficiently and cost-effectively on cloud-based storages. In addition, cheap computer memory and improved network speeds also provided the advantage to big data stage.
With all these technology transitions, it is now possible to imagine ways the companies can leverage data that would not have been conceivable a decade back.
Big Data is a mixture of technologies such as virtualization, parallel processing, distributed file system and in-memory databases which have been around for decades and technologies like Hadoop, MapReduce, Spark etc which are relatively new. This combination of technology advances can now solve significant business cases which were not possible before.
Now organizations can process petabytes of data with acceptable performance to detect patterns and anomalies to make sense of data and generate value. Science and research are also benefitting from these advancements, for example, analyzing the human genome or processing astronomical data collected at observatories.
For someone new into Big Data, this article “Big Data: A Beginner’s Guide for Non-Technical People” is a great start.
Final Thoughts
Different approaches to handle data exists within the big data ecosystem. The technologies required to get the answers the businesses needs are still isolated from each other and depends on use cases. To get to the desired end state, the technologies need to converge and that is what is happening in the big data ecosystem now. So to conclude, we can say the big data is not a single technology but a combination of old and new technologies which are converging to help organizations gain actionable insights and generate business values. Therefore, big data is the capability to manage a huge volume of disparate data, at the right speed and within the right time frame to allow real-time analysis and reaction.

[…] Image Credits: Contemplating Data […]